The electron configuration is the formula for the location of electrons in the various electron shells of an atom of a chemical element or molecule. The electron configuration is usually written for atoms in their ground state.
The following rules exist for determining the electronic configuration of an element.
1. The Principles of Filling
According to the filling principle, electrons in the ground state of an atom fill the orbitals in the sequence of increasing orbital energy levels.
2. Pauli's Inhibition Principle
According to this principle, no more than two electrons can be on any orbital.
3. The Hund Principle
According to this rule, the filling of the orbitals of one subshell begins with single electrons, and only after the single electrons occupy all the orbitals can the final filling of the orbitals with electron pairs take place.
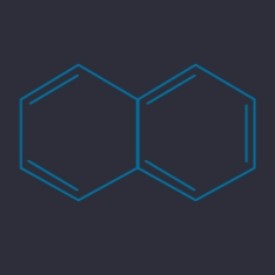
Naphthalene
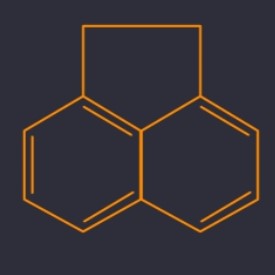
Acenaphthene
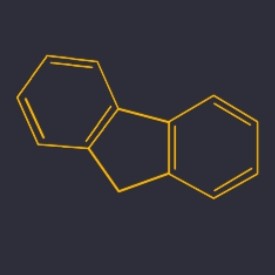
Fluorene

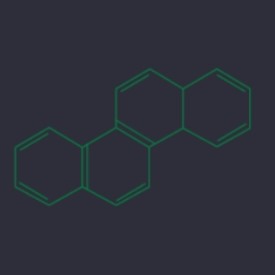
Phenanthrene

Anthracene
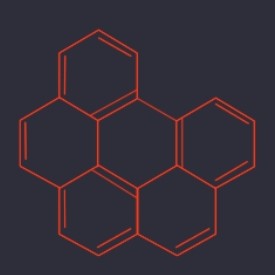
Benzo(ghi)perylene

Pyrene
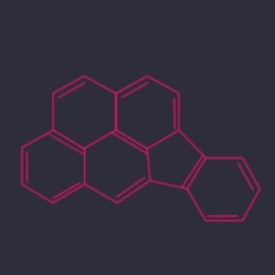
Indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene
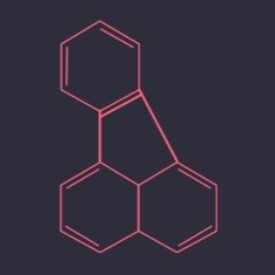
Fluoranthene
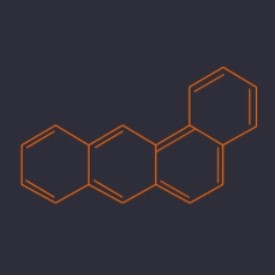
Benzo(α)anthracene

Benzo(k)Fluoranthene
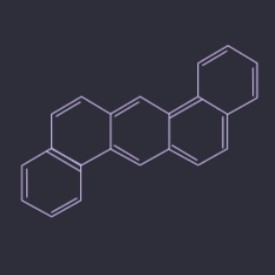
Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene